by Colin Harper | Jun 26, 2024 | New Product, News
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Houston, TX, [June 20, 2024] – BPM Microsystems, Inc., a global leader in device programming solutions, is proud to announce the launch of the BPM210, the world’s first semi-automatic universal production programmer (patent pending). This groundbreaking innovation sets a new standard for productivity, operator safety, and device support in the high-volume production programming industry.
The BPM210 boasts cutting-edge features, including electric motors that automatically open and close sockets, reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries and increasing throughput. With the ability to program up to 8 devices simultaneously using BPM’s 10th Gen technology, the BPM210 delivers unmatched programming speed and efficiency. Time studies indicate the semi-automatic programmer provides more than double the production throughput compared to typical manual programming, where the operator has to open and close the sockets individually.
“We are thrilled to introduce the BPM210, a testament to our commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction,” said William White, President and CEO of BPM Microsystems, Inc. “We are confident this semi-automatic solution will revolutionize how our customers approach manual high-volume production programming, enabling them to achieve new productivity, safety, and profitability levels.
The BPM210 supports various device types through its extensive range of socket adapters, ensuring universal device support. BPM’s active socket adapters feature controlled impedance signal paths, providing superior signal integrity compared to DIP adapters. The programmer is designed for seamless integration and ease of use, with quick setup and changeover requiring no tools and the ability to connect multiple units to the same PC for parallel operation. With this expanded capacity, a single operator can program millions of devices annually.
Designed and manufactured in an ISO 9001:2015 certified facility, the BPM210 is CE Mark Safety Directive compliant and has a comprehensive 1-year warranty. The diagnostics card allows easy troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance. The BPM210 has been meticulously designed with ESD safety in mind, featuring a banana jack for a grounding wrist strap and static dissipative cover and surfaces, ensuring a safe and reliable programming environment.
The BPM210 was demonstrated at SMTconnect 2024 in Nuremberg, Germany, and was well-received by attendees. It is now available for order. For more information about the BPM210, visit www.www.bpmmicro.com or contact BPM Microsystems’ Sales at Inside_Sales@bpmmicro.com.
About BPM Microsystems, Inc.
Founded in 1985, BPM Microsystems is a global supplier of electronic device programming systems, software, and solutions. Headquartered in Houston, Texas, BPM Microsystems has an international presence through its extensive distribution partners in Europe, Asia, and the Americas. The company’s innovative programming solutions are designed to meet the demanding requirements of high-volume production programming, enabling customers to achieve the highest levels of productivity, quality, and reliability.
Contact:
[Colin Harper ]
[Director of Product Management]
BPM Microsystems, Inc.
[716-688-4600]
[Colin_Harper@bpmmicro.com]

by Scott Bronstad | Sep 11, 2023 | New Product, Video, Virtual Demo
Video: BPM Microsystems Automated Labeler Peripheral
Unveiling the Future of Device Labeling: Introducing BPM Microsystems’ Automated Labeler Peripheral for 3X and 4X Series
We take a dive into BPM Microsystems’ Automated Labeler Peripheral. Say goodbye to manual labeling and say hello to a streamlined, automated solution designed specifically for BPM 3X and 4X series automated programmers.
🌟 Features & Benefits:
📏 Size Versatility: The Automated Labeler handles label sizes ranging from a petite 3mm x 3mm, all the way up to 30x30mm, accommodating even the largest QFPs.
📜 Pre-printed or Blank Labels: You have the flexibility to use either pre-printed labels or blank labels, giving you the power to decide how your labeling process will go.
🔨 Quick & Easy Installation: Say goodbye to complicated setups. Installing the Automated Labeler is as simple as installing a tape feeder, making it an efficient add-on to your existing setup.
💲 Cost-Effective: A budget-friendly, one-time investment that pays dividends by ensuring traceability and quality assurance.
Enhanced Traceability: Add an extra layer of verification to ensure each device has been programmed correctly. Improve your workflow while adhering to quality standards.
🛠 Specifications:
Compatible With: BPM Microsystems 3X and 4X Series Automated Programmers
Label Size Range: 3mm x 3mm to 30mm x 30mm
Installation: Quick/easy, akin to a tape feeder
Pricing: Affordable initial investment
🔑 Why Choose the BPM Microsystems Automated Labeler?
This game-changing peripheral is an essential addition to your automated programming workflow. If you’re looking to boost your operational efficiency while also adding a robust layer of traceability, then look no further.
by Scott Bronstad | Feb 28, 2023 | Case Study, Product Comparison, Technology
Semiconductor devices are used in a wide range of electronic applications, from smartphones to industrial machinery. Programming these devices is a crucial step in their manufacturing process, allowing them to perform specific functions. There are several methods to program semiconductor devices, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
In-System Programming (ISP)

Bed-of-Nails fixture connects the PCB to the final test
In-system programming (ISP) is a method that enables semiconductor devices to be programmed after installation on a circuit board, without requiring removal. This programming method allows for easy updates, and flexibility in the programming process, and avoids device disruption. However, ISP requires dedicated programming hardware or software to interface with the device, which may be slower than other methods. Moreover, when the programming process exceeds a few seconds, it can create bottlenecks, slowing down the production line and making it harder to scale. Learn more here.
In-Circuit Programming (ICP)
In-circuit programming (ICP) is a method that enables semiconductor devices to be programmed while they are in use, without requiring removal. This programming method allows for updates without disrupting device operation, flexibility in the programming process, and avoids device removal. However, ICP requires dedicated programming hardware or software to interface with the device, which may be slower than other methods. Learn more here.
Offline Parallel Programming
Offline programming is a method that enables multiple semiconductor devices to be programmed simultaneously. This programming method is faster than ISP and ICP, allows for a high volume of devices to be programmed at once, and can be easily scaled up. Offline programming requires a dedicated socket adapter with a custom algorithm for each device type. For instance, a socket receptacle can accept similar device types from different manufacturers (for example, a BGA(153), but will require a custom algo for each device to ensure it meets the specs for that device).
 Automated Offline Programming
Automated Offline Programming
Automated programming is a subset of offline programming that uses automated equipment to program semiconductor devices. This programming method is faster than development kits and allows for a high volume of devices to be programmed simultaneously. Moreover, automated programming allows for individual device programming, and is more easily scaled by adding additional resources and shifts.
Development Kits
 Device programming kits are tools used to program individual semiconductor devices. This programming method allows for individual device programming and prototyping. However, development kits can be slower than other methods and require manual device handling, which can be time-consuming and error-prone. If a prototype goes into full production, other methods should be explored, which will require first article proofing for the production programmer.
Device programming kits are tools used to program individual semiconductor devices. This programming method allows for individual device programming and prototyping. However, development kits can be slower than other methods and require manual device handling, which can be time-consuming and error-prone. If a prototype goes into full production, other methods should be explored, which will require first article proofing for the production programmer.
In conclusion, choosing the right programming method for your programmable devices depends on your specific needs and requirements. Consider the pros and cons of each method before making a decision. Ultimately, selecting the right programming method can save you time and costs while ensuring your devices function properly.
Programming Method
|
Definition
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
Approx. Usage
|
| In-System Programming (ISP) |
Programming a device after it has been installed on a circuit board, without needing to remove it |
Allows for easy updates in the field, avoids device removal, and provides flexibility in the programming process |
Requires dedicated programming hardware or software to interface with the device, which may be slower than other methods |
40% |
| In-Circuit Programming (ICP) |
Programming a device while it is in use, without needing to remove it |
Allows for updates without disrupting device operation, avoids device removal, and provides flexibility in the programming process |
Requires dedicated programming hardware or software to interface with the device, which may be slower than other methods. |
20% |
| Offline Parallel Programming |
Simultaneously programming multiple devices with the same programming sequence using specialized equipment |
Efficient for large-scale production, automated to increase throughput, and reduces programming errors |
Requires specialized equipment that may be relatively expensive, and less flexible for smaller production runs |
25% |
| Development Kits |
Dedicated hardware and software used to program a single device at a time, typically used for low-volume production or prototyping |
Provides a high degree of control and flexibility over the programming process, can program a wide range of devices, suitable for low-volume production or prototyping |
Requires dedicated hardware and software that is typically inexpensive, and time-consuming for large-scale production or programming of multiple devices with different programming sequences |
15% |
Note: The percentages provided are rough estimates and may vary depending on the specific industry and application.

by Scott Bronstad | Nov 19, 2021 | Events, New Product, News, Trade Shows
Productronica 2021 ends with about 20,000 visitors and 894 exhibitors from 36 countries (including BPM), underscoring its position as a leading trade fair for the electronics industry. While those numbers are down from previous shows, there was much pent-up interest. Those who were there were eager to see what’s new. Read more here.
 The new BPM310 10th Generation Automated Programmer ran flawlessly. Final numbers for the demo: 1,200 Devices per Hour (DPH) on four 10th Gen Sites with 32 sockets tray-to-tray (TS1500 Tray Stacker). The benchmark devices were BGA153s with a programming time of 38 seconds. By the fourth day of Productronica, the BPM310 cycled through over 30,000 devices! The BPM310 has a maximum configuration of 48 sockets on a smaller platform, with a maximum DPH of 1,432. The BPM310 can be configured with advanced peripherals, such as 3D inspection and fiber laser marker.
The new BPM310 10th Generation Automated Programmer ran flawlessly. Final numbers for the demo: 1,200 Devices per Hour (DPH) on four 10th Gen Sites with 32 sockets tray-to-tray (TS1500 Tray Stacker). The benchmark devices were BGA153s with a programming time of 38 seconds. By the fourth day of Productronica, the BPM310 cycled through over 30,000 devices! The BPM310 has a maximum configuration of 48 sockets on a smaller platform, with a maximum DPH of 1,432. The BPM310 can be configured with advanced peripherals, such as 3D inspection and fiber laser marker.
“Another Productronica is in the record books,” says Colin Harper, Global Sales Director at BPM. “A big thanks to Adaptsys (BPM’s European Distributor) for another successful show. And thank you to all the visitors that stopped by to see our new universal automated programming system, the BPM310. We’re looking forward to furthering engagement. Prost!”
The BPM310 was received well by numerous electronics manufacturers, who are interested in bringing programming in-house. They are excited by the prospect of a small platform with maximum capacity, including high-density devices, such as eMMC, UFS, and Microcontrollers without the need for multiple site types.
Next Productronica, which happens every two years, will be November 14-17 2023.

by Scott Bronstad | Nov 17, 2021 | Events, New Product, News, Trade Shows
 Day 2 is in the books: more traffic and lots of excitement for BPM’s latest innovation, the BPM310 Automated Programmer. Automotive, Contract Manufacturers and Consumer Electronics companies are among those interested.
Day 2 is in the books: more traffic and lots of excitement for BPM’s latest innovation, the BPM310 Automated Programmer. Automotive, Contract Manufacturers and Consumer Electronics companies are among those interested.
The BPM310 is positioned to outperform higher-priced systems and includes advanced features such as WhisperTeach™, on-the-fly vision alignment, CSP support, serialization, encryption, and JobMaster while providing true universal technology. 10th Generation site technology supports the broadest range of devices including MCUs, eMMC, NAND, Serial Flash, UFS, and others. Highly configurable, the BPM310 provides options for Tape I/O, Tray I/O, Tube I/O, laser marking, and 3D inspection.
Productronica in Munich Germany is the second-largest electronics trade show in the world and continues through November 19, 2021.
Learn about BPM310 | US Tech Article | BPM310 Press Release
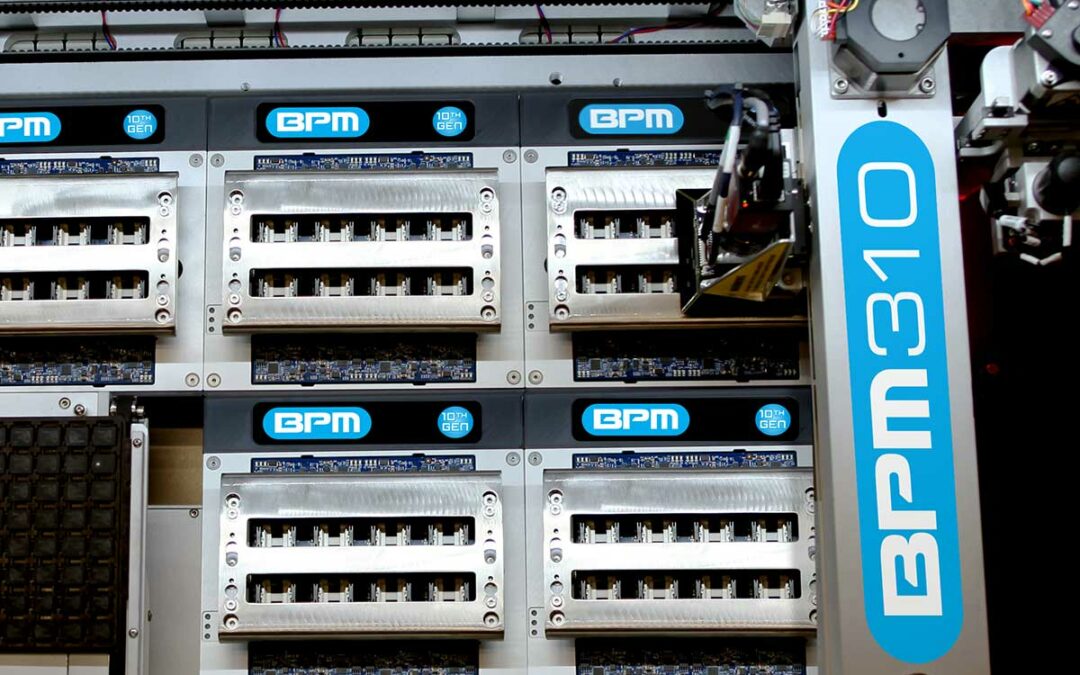

by Scott Bronstad | Nov 16, 2021 | Announcements, Featured, New Product, News
 BPM Microsystems, Inc. announces the release of its 10th Generation programming technology platform and the BPM310 Automated Programming System. The 10th Generation offers the industry’s fastest programming times for UFS, eMMC, Flash, and MCUs with twice as many sockets per site as its predecessor. The BPM310 offers a capacity of up to 48 sockets, automotive-level quality, and reliability in a small footprint. 10th Gen delivers the fastest UFS programming performance in the industry achieving up to 440MB per second Read and 201MB per second Write. First-part time is accelerated because UFS programming can commence without pausing for data to download.
BPM Microsystems, Inc. announces the release of its 10th Generation programming technology platform and the BPM310 Automated Programming System. The 10th Generation offers the industry’s fastest programming times for UFS, eMMC, Flash, and MCUs with twice as many sockets per site as its predecessor. The BPM310 offers a capacity of up to 48 sockets, automotive-level quality, and reliability in a small footprint. 10th Gen delivers the fastest UFS programming performance in the industry achieving up to 440MB per second Read and 201MB per second Write. First-part time is accelerated because UFS programming can commence without pausing for data to download.
The BPM310 is positioned to outperform higher-priced systems and includes advanced features such as WhisperTeach™, on-the-fly vision alignment, CSP support, serialization, encryption, and JobMaster while providing true universal technology. 10th Gen supports the broadest range of devices including MCUs, eMMC, NAND, Serial Flash, UFS, and others. Highly configurable, the BPM310 provides options for Tape I/O, Tray I/O, Tube I/O, laser marking, and 3D inspection.
“Our engineering team has done an amazing job creating the most powerful universal programmer in the industry. Unlike competitive products, our system offers true universal support including CSP, Flash, MCUs, eMMC, and UFS with up to 8 sockets per site to deliver unbeatable system value,” says William White, founder and CEO of BPM Microsystems. “The BPM310 is now our flagship product with the greatest capacity, flexibility, features, reliability, and smallest footprint in our product line.”
“We’re excited to showcase the BPM310 at Productronica and anticipate a positive market response,” says Colin Harper, Global Sales Director at BPM. “In the past, we have demonstrated two machines at the trade show. Now we have one system that can do it all. In fact, the BPM310 is able to program as many devices concurrently as our larger system, the 4910, in a footprint about half its size while offering the same I/O flexibility and improved reliability.”
The BPM310 leverages much of the socket adapter and algorithm development currently available on its 9th Generation systems. And like all 9th Gen automated programmers, the BPM310 continues to offer ease of operation and fast setup with award-winning BPWin process control software and patented WhisperTeach™. WhisperTeach™ automatically teaches the critical Z-height of each pick/place location with 15-micron accuracy. Accurate automated teaching is vital for small packages due to fundamental human limitations. Plus WhisperTeachTM saves an average of 83% of the time required for the job setup compared to traditional methods while increasing quality and yield.
 BPM manufactures its 10th Generation systems in their ISO 9001:2015 certified plant located in Houston, Texas, and their products carry the CE Mark. BPM continues to offer 9th Generation programmers for manual and automated programming. If you are at Productronica 2021, visit Hall A1-353 from November 16 through 19, 2021 to see a live BPM310 demo. For more information on the BPM310, go to www.bpmmicro.com/BPM310.
BPM manufactures its 10th Generation systems in their ISO 9001:2015 certified plant located in Houston, Texas, and their products carry the CE Mark. BPM continues to offer 9th Generation programmers for manual and automated programming. If you are at Productronica 2021, visit Hall A1-353 from November 16 through 19, 2021 to see a live BPM310 demo. For more information on the BPM310, go to www.bpmmicro.com/BPM310.



 Automated Offline Programming
Automated Offline Programming Device programming kits are tools used to program individual semiconductor devices. This programming method allows for individual device programming and prototyping. However, development kits can be slower than other methods and require manual device handling, which can be time-consuming and error-prone. If a prototype goes into full production, other methods should be explored, which will require first article proofing for the production programmer.
Device programming kits are tools used to program individual semiconductor devices. This programming method allows for individual device programming and prototyping. However, development kits can be slower than other methods and require manual device handling, which can be time-consuming and error-prone. If a prototype goes into full production, other methods should be explored, which will require first article proofing for the production programmer.
 The new
The new 
 Day 2 is in the books: more traffic and lots of excitement for BPM’s latest innovation, the
Day 2 is in the books: more traffic and lots of excitement for BPM’s latest innovation, the 